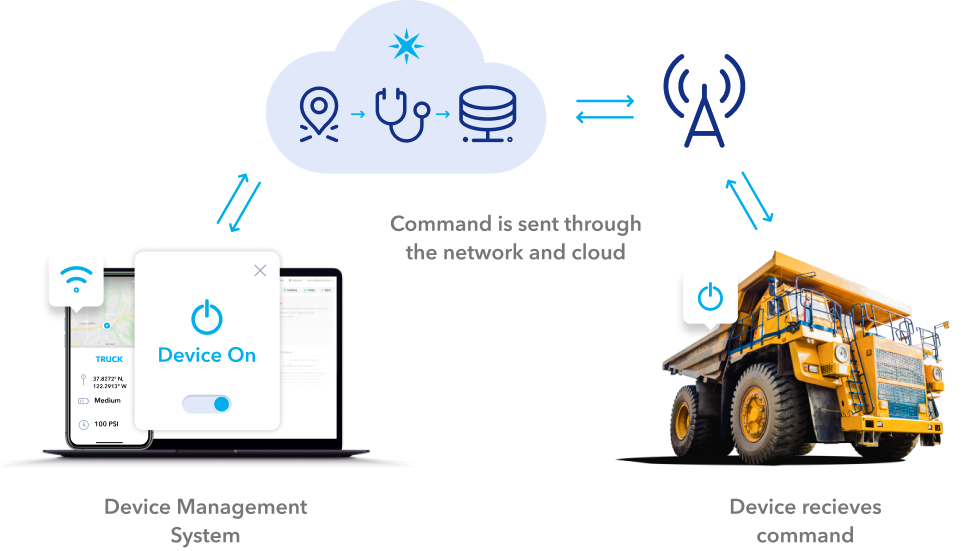
Can you imagine a world where you can manage and control devices across vast distances, all from the convenience of a single interface? The answer is already here, and it's called remote management in the Internet of Things (IoT). This technology is reshaping how we interact with technology, offering unprecedented control and efficiency.
The relentless march of technological advancement has paved the way for the Internet of Things (IoT) to become a ubiquitous force in our lives. From the smallest sensor to the most complex industrial machinery, devices are now interconnected, exchanging data and communicating seamlessly. This interconnectedness, however, presents a significant challenge: how do we manage and maintain these myriad devices effectively? The answer lies in remote management, a powerful suite of tools and strategies that allow businesses and individuals to monitor, control, and troubleshoot IoT devices from anywhere in the world. This shift is not just about technological advancement; it is about a fundamental change in how we approach efficiency, security, and operational control. As we move deeper into this connected era, understanding the nuances and potential of remote management is becoming increasingly crucial.
The evolution of remote management within the IoT ecosystem is marked by several key phases. Initially, the focus was on basic connectivity, allowing devices to simply transmit data. Then, with the advent of the internet, came the ability to monitor these devices. As technology progressed, remote control emerged, enabling users to make changes to devices from afar. Today, the trend is towards more sophisticated solutions that incorporate artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics to automate tasks, predict potential issues, and optimize performance. This continuous innovation ensures that remote management will remain at the forefront of technological advancement.
- Kash Patels Eye Injury What Happened Why It Matters
- Hd4hub Hindi Dubbed Movies What You Need To Know Guide
The Evolution of Remote Management in IoT
The development of remote management in IoT is an ongoing journey, marked by several significant stages. This table presents a chronological overview of the most impactful advancements and milestones:
| Year | Development | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early 1990s | Emergence of the Internet and Networking Protocols | Provided the foundational infrastructure for remote communication between devices. |
| Late 1990s - Early 2000s | Development of Embedded Systems and Early IoT Devices | Enabled the creation of devices capable of collecting and transmitting data, paving the way for rudimentary remote monitoring. |
| Mid-2000s | Growth of Broadband and Wireless Technologies (Wi-Fi, Cellular) | Improved connectivity and bandwidth, facilitating more complex remote management tasks. |
| Late 2000s - Early 2010s | Introduction of Cloud Computing Platforms | Provided scalable infrastructure and data storage solutions to support the management of large numbers of IoT devices. |
| Mid-2010s | Advancements in Security Protocols and Encryption | Increased the security of remote management systems, addressing concerns about data breaches and unauthorized access. |
| Late 2010s - Present | Integration of AI and Machine Learning, Edge Computing | Allowed for predictive maintenance, automated device management, and real-time data analysis, optimizing performance and efficiency. |
| Present | 5G and Enhanced Connectivity | Offering faster and more reliable connectivity, enabling more sophisticated and bandwidth-intensive remote management applications. |
Introduction to IoT and Remote Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with technology. It refers to a vast network of interconnected devices, ranging from simple sensors to complex industrial machinery, all capable of communicating and exchanging data without human intervention. This interconnectedness is achieved through embedded systems, software, sensors, and other technologies that enable devices to collect, transmit, and analyze data in real-time. Remote management, in this context, is the art and science of controlling and monitoring these devices from a distance. It empowers businesses and individuals to maintain oversight, ensure optimal performance, and address issues swiftly and efficiently, regardless of the physical location of the device.
The increasing prevalence of IoT devices has led to the rise of remote management as an essential component of modern technological infrastructure. The ability to perform tasks such as firmware updates, troubleshooting, and data analysis without the need for physical presence is invaluable in industries where geographic dispersion is a challenge, such as agriculture, logistics, and healthcare. Through remote management, businesses can reduce operational costs, increase efficiency, and improve decision-making based on real-time data analysis. This, in turn, leads to greater profitability and enhanced competitiveness in the market. Furthermore, remote management facilitates faster response times and enables proactive maintenance, contributing significantly to operational stability and longevity of the connected devices.
- Kate Hudsons Political Views A Deep Dive Explained
- Decoding The Pining For Kim Video Origins Impact Why It Matters
Benefits of Remote Management in IoT
The implementation of remote management in IoT offers a multitude of advantages that can have a significant impact on business operations. These benefits extend beyond mere convenience, offering tangible improvements in efficiency, cost savings, security, and scalability. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: Automating device management reduces the need for manual intervention, saving time and resources. This automation simplifies tasks such as software updates, configuration changes, and diagnostics, allowing IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Cost Reduction: By minimizing the need for on-site visits, businesses can cut down on travel and maintenance expenses. Remote diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities prevent the need for physical interventions, saving on labor and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Security: Remote management tools often come equipped with advanced security features, ensuring the protection of sensitive data. These features include secure authentication protocols, encryption, and regular security updates. Centralized security management further reduces the risks associated with potential threats.
- Improved Scalability: Businesses can easily scale their IoT ecosystems as needed without worrying about the logistical challenges of managing a growing number of devices. This scalability provides the flexibility to adapt to changing business demands, add new devices, and expand the network with minimal operational disruption.
Real-World Remote Management in IoT Examples
To better understand the practical applications of remote management in IoT, let's delve into some real-world examples across various industries. These examples demonstrate the versatility and transformative potential of remote management.
Smart Home Management
Smart homes are a quintessential example of how remote management in IoT enhances everyday life. Homeowners can control lighting, heating, security systems, and appliances from their smartphones or tablets, regardless of their physical location. This level of control enhances convenience and promotes energy efficiency and cost savings. The ability to remotely monitor energy consumption, adjust thermostats, and manage security systems provides homeowners with significant control over their living environments.
Industrial Automation
In the industrial sector, remote management of IoT devices is critical for maintaining operational continuity. Manufacturers can monitor the performance of machinery, detect potential issues, and perform predictive maintenance to minimize downtime. This approach not only improves productivity but also extends the lifespan of equipment. Remote diagnostics capabilities allow engineers to identify and resolve issues before they escalate, while predictive maintenance enables proactive repairs, resulting in optimized operational efficiency and minimizing disruption.
Supply Chain Management
Remote management plays a crucial role in supply chain management, facilitating real-time tracking of goods, monitoring environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), and ensuring the timely delivery of products. Companies can track shipments, optimize routes, and manage inventory effectively through sensor-based tracking systems and cloud-based monitoring platforms. This visibility streamlines operations and enhances responsiveness to disruptions, from the factory floor to the end customer.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, remote patient monitoring has transformed how medical professionals provide care. By using wearable devices and remote monitoring systems, healthcare providers can monitor patients' vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, from anywhere. This allows for proactive intervention and early detection of potential health issues, contributing to better patient outcomes and reducing the burden on healthcare facilities.
Agriculture
Remote management is employed extensively in precision agriculture. Farmers use IoT sensors to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. Data is used to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. The result is optimized resource utilization, higher crop yields, and reduced environmental impact. Through automation and remote monitoring, farmers can also manage complex farming operations with greater efficiency and less manual labor.
Retail
Retailers utilize remote management to monitor and manage various aspects of their operations. This includes managing energy consumption in stores, optimizing inventory levels, and ensuring the proper functioning of point-of-sale (POS) systems. Through remote monitoring and control, retailers can ensure operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer experience.
Transportation
Remote management is crucial in the transportation sector for fleet management. Companies use IoT devices to track vehicle location, monitor driver behavior, and optimize routes. By collecting and analyzing data from vehicles, transportation companies can improve efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, and enhance safety.
Security Considerations in Remote Management
While remote management in IoT offers numerous benefits, it also introduces security challenges that must be addressed. The security of IoT devices is paramount, as they often handle sensitive data and are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting these devices and the data they generate. Here are key considerations:
- Implement robust authentication protocols to prevent unauthorized access: This can involve multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and regular password updates. Authentication verifies the identity of users and devices attempting to connect to the network, preventing unauthorized access.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch security vulnerabilities: Software and firmware updates should be a priority to address known security flaws and vulnerabilities. Keeping the software current minimizes the risk of exploitation by attackers.
- Encrypt data transmissions to protect information from interception: Encryption ensures that data transmitted between devices and servers is unreadable to unauthorized parties. Encryption protects sensitive information from interception and ensures data privacy.
- Secure network infrastructure: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other network security measures to protect the IoT devices and the network itself. These measures help to identify and mitigate potential security threats.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments: Regular audits and assessments help identify weaknesses in the system. These audits help ensure the effectiveness of security measures and ensure the overall security posture.
- Establish incident response plans: Preparedness for security incidents is essential. Develop plans to identify, contain, eradicate, and recover from security breaches, ensuring minimal disruption to the system.
Tools and Platforms for Remote Management
Several tools and platforms are available to facilitate remote management in IoT. These solutions offer a user-friendly interface for monitoring and controlling devices, making it easier for businesses to manage their IoT ecosystems. Here are some popular options:
- Microsoft Azure IoT Hub: A cloud-based platform supporting scalable IoT solutions and robust security features. It provides device management, data ingestion, and advanced analytics capabilities.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT Core: A fully managed service enabling secure and reliable communication between IoT devices and the cloud. It provides a scalable platform with features such as device authentication, data encryption, and device management.
- IBM Watson IoT Platform: A comprehensive platform that integrates IoT data with advanced analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities. It enables organizations to gain insights from their IoT data through machine learning and predictive analytics.
- Google Cloud IoT Platform: A fully managed platform for securely connecting, managing, and processing data from globally dispersed devices. It offers end-to-end security, device management, and integration with Google Cloud services.
- ThingWorx: An industrial IoT platform that provides tools for developing and deploying IoT applications. It offers a comprehensive set of capabilities for device connectivity, data management, and application development.
Challenges in Remote Management
Despite its many advantages, remote management in IoT is not without its challenges. Navigating these obstacles is crucial for successful implementation and long-term sustainability. Some of the common obstacles include:
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring that devices from different manufacturers can communicate effectively can be a complex task. Devices from diverse manufacturers often use varying communication protocols, leading to compatibility issues. Standardizing protocols and incorporating open-source technologies is essential for ensuring seamless communication.
- Network Reliability: Dependence on stable internet connectivity can be a limitation, especially in remote areas. Areas with poor or unstable internet connectivity will significantly affect remote management capabilities. Solutions such as satellite internet, cellular connectivity, and edge computing can help mitigate this.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Protecting user data from unauthorized access and misuse is a top priority for IoT developers. Data breaches and privacy violations can erode trust and lead to significant legal and reputational consequences. Adherence to data privacy regulations and the implementation of robust security measures are essential for building and maintaining trust.
- Scalability Issues: Managing a growing number of devices can become complicated, especially as an IoT ecosystem expands. Scaling the infrastructure to handle increased data volume and device management requires thoughtful planning. Cloud-based platforms and scalable architecture are vital to managing larger networks.
- Security Breaches and Cyberattacks: Vulnerability to cyberattacks is a major concern for IoT devices. Devices may be compromised, resulting in unauthorized data access, manipulation, and disruption. Implementing robust security measures, including frequent updates and encryption, is essential for mitigating these risks.
- Lack of Standardization: The absence of a standard for IoT device communication and management can make it challenging to integrate devices from different vendors. This necessitates the adoption of industry-standard protocols to improve interoperability.
Future Trends in Remote Management
The field of remote management in IoT is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology and shifting market demands. These emerging trends will shape the future of remote management, offering increased capabilities and enhanced efficiency. Some of the emerging trends to watch include:
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source reduces latency and improves real-time decision-making. Edge computing is key for applications requiring low latency and high responsiveness.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven analytics can enhance predictive maintenance and optimize device performance. AI enables automated device management, predictive maintenance, and intelligent data analytics.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks promises to revolutionize IoT by providing faster and more reliable connectivity. 5G offers increased bandwidth, which enhances the performance of connected devices and applications, particularly in areas with high-density deployments.
- Blockchain Technology: Integrating blockchain for secure data transactions and device authentication. Blockchain offers enhanced security and transparency, which helps address security concerns.
- Digital Twins: Creating virtual replicas of physical assets to monitor and simulate their behavior in real-time. Digital twins are leveraged for predictive maintenance, optimization, and improving asset performance.
- Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN): Using LPWAN technologies, such as LoRaWAN and NB-IoT, for long-range, low-power connectivity in remote or challenging environments. LPWANs expand the reach of IoT networks in areas where traditional network connectivity is not feasible.
Best Practices for Effective Remote Management
To maximize the benefits of remote management in IoT, it's essential to follow best practices. These recommendations provide a comprehensive guide to effective implementation and management.
- Develop a clear strategy for deploying and managing IoT devices: A well-defined strategy is essential. The plan should encompass objectives, target devices, desired functionalities, and security considerations.
- Invest in reliable and scalable infrastructure to support your IoT ecosystem: Reliable and scalable infrastructure is critical for seamless operation. This includes selecting appropriate cloud platforms, networking, and hardware solutions.
- Regularly review and update your security protocols to stay ahead of potential threats: Security is always evolving, and its crucial to remain vigilant. Regularly review security protocols, conduct security audits, and apply regular updates to address vulnerabilities.
- Prioritize data privacy and compliance with regulations: Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is non-negotiable. Organizations must implement robust data protection mechanisms and ensure data privacy.
- Implement Over-the-Air (OTA) firmware updates: This ensures that devices stay updated with the latest security patches and performance enhancements. OTA updates simplify device management and improve overall security.
- Use centralized management platforms: Using these platforms offers a comprehensive view of the entire IoT ecosystem. These platforms streamline management and enable centralized control.
- Regularly monitor device health and performance: Proactive monitoring helps to detect potential issues. Regular monitoring helps in preventive maintenance.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Several organizations have successfully implemented remote management in IoT, achieving significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and operational excellence. These case studies provide real-world examples of the transformative potential of remote management.
- John Deere: The agricultural giant uses IoT technology to monitor and manage farm equipment remotely, optimizing operations and reducing costs. Through remote monitoring, John Deere provides farmers with real-time data on the equipment's performance. The data facilitates proactive maintenance, optimizes fuel consumption, and minimizes downtime.
- Nest: The smart thermostat company allows users to control their home heating and cooling systems from anywhere, promoting energy efficiency and convenience. The Nest system enables homeowners to adjust temperatures and monitor energy consumption remotely using their smartphones. The insights Nest provides improve energy usage and lower utility costs.
- Tesla: The electric vehicle manufacturer uses remote diagnostics and over-the-air updates to improve vehicle performance and address issues. Tesla is able to update vehicle software remotely, enhance the performance of its vehicles, and address any issues that arise.
- Rolls-Royce: The aerospace giant employs remote monitoring and predictive maintenance for aircraft engines, enhancing operational efficiency. Rolls-Royce can predict potential engine failures and adjust maintenance schedules, improving aircraft uptime and lowering operational costs.
These case studies show the broad applicability and impact of remote management in IoT across diverse sectors, from agriculture to the energy, healthcare, manufacturing, and consumer electronics industries. Each implementation represents a significant step forward in efficiency, cost savings, and operational optimization.
- Slope Game Unblocked 76 Your Ultimate Guide To Success
- Avoid 5movierulz Is Kannada Movie Download Legal Safe In 2023